1) What do you understand by Machine learning?
Machine learning is the form of Artificial Intelligence that deals with system programming and automates data analysis to enable computers to learn and act through experiences without being explicitly programmed.
For example, Robots are coded in such a way that they can perform the tasks based on data they collect from sensors. They automatically learn programs from data and improve with experiences.
2) Differentiate between inductive learning and deductive learning?
In inductive learning, the model learns by examples from a set of observed instances to draw a generalized conclusion. On the other side, in deductive learning, the model first applies the conclusion, and then the conclusion is drawn.
- Inductive learning is the method of using observations to draw conclusions.
- Deductive learning is the method of using conclusions to form observations.
For example, if we have to explain to a kid that playing with fire can cause burns. There are two ways we can explain this to a kid; we can show training examples of various fire accidents or images of burnt people and label them as "Hazardous". In this case, a kid will understand with the help of examples and not play with the fire. It is the form of Inductive machine learning. The other way to teach the same thing is to let the kid play with the fire and wait to see what happens. If the kid gets a burn, it will teach the kid not to play with fire and avoid going near it. It is the form of deductive learning.
3) What is the difference between Data Mining and Machine Learning?
Data mining can be described as the process in which the structured data tries to abstract knowledge or interesting unknown patterns. During this process, machine learning algorithms are used.
Machine learning represents the study, design, and development of the algorithms which provide the ability to the processors to learn without being explicitly programmed.
4) What is the meaning of Overfitting in Machine learning?
4) What is the meaning of Overfitting in Machine learning?
Overfitting can be seen in machine learning when a statistical model describes random error or noise instead of the underlying relationship. Overfitting is usually observed when a model is excessively complex. It happens because of having too many parameters concerning the number of training data types. The model displays poor performance, which has been overfitted.
5) Why overfitting occurs?
The possibility of overfitting occurs when the criteria used for training the model is not as per the criteria used to judge the efficiency of a model.
6) What is the method to avoid overfitting?
Overfitting occurs when we have a small dataset, and a model is trying to learn from it. By using a large amount of data, overfitting can be avoided. But if we have a small database and are forced to build a model based on that, then we can use a technique known as cross-validation. In this method, a model is usually given a dataset of a known data on which training data set is run and dataset of unknown data against which the model is tested. The primary aim of cross-validation is to define a dataset to "test" the model in the training phase. If there is sufficient data, 'Isotonic Regression' is used to prevent overfitting.
7) Differentiate supervised and unsupervised machine learning.
- In supervised machine learning, the machine is trained using labeled data. Then a new dataset is given into the learning model so that the algorithm provides a positive outcome by analyzing the labeled data. For example, we first require to label the data which is necessary to train the model while performing classification./li>
- In the unsupervised machine learning, the machine is not trained using labeled data and let the algorithms make the decisions without any corresponding output variables.
8) How does Machine Learning differ from Deep Learning?
- Machine learning is all about algorithms which are used to parse data, learn from that data, and then apply whatever they have learned to make informed decisions.
- Deep learning is a part of machine learning, which is inspired by the structure of the human brain and is particularly useful in feature detection.
9) How is KNN different from k-means?
KNN or K nearest neighbors is a supervised algorithm which is used for classification purpose. In KNN, a test sample is given as the class of the majority of its nearest neighbors. On the other side, K-means is an unsupervised algorithm which is mainly used for clustering. In k-means clustering, it needs a set of unlabeled points and a threshold only. The algorithm further takes unlabeled data and learns how to cluster it into groups by computing the mean of the distance between different unlabeled points.
10) What are the different types of Algorithm methods in Machine Learning?
The different types of algorithm methods in machine earning are:
- Supervised Learning
- Semi-supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Transduction
- Reinforcement Learning
11) What do you understand by Reinforcement Learning technique?
Reinforcement learning is an algorithm technique used in Machine Learning. It involves an agent that interacts with its environment by producing actions & discovering errors or rewards. Reinforcement learning is employed by different software and machines to search for the best suitable behavior or path it should follow in a specific situation. It usually learns on the basis of reward or penalty given for every action it performs.
12) What is the trade-off between bias and variance?
Both bias and variance are errors. Bias is an error due to erroneous or overly simplistic assumptions in the learning algorithm. It can lead to the model under-fitting the data, making it hard to have high predictive accuracy and generalize the knowledge from the training set to the test set.
Variance is an error due to too much complexity in the learning algorithm. It leads to the algorithm being highly sensitive to high degrees of variation in the training data, which can lead the model to overfit the data.
To optimally reduce the number of errors, we will need to tradeoff bias and variance.
13) How do classification and regression differ?
| Classification | Regression |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14) What are the five popular algorithms we use in Machine Learning?
Five popular algorithms are:
- Decision Trees
- Probabilistic Networks
- Neural Networks
- Support Vector Machines
- Nearest Neighbor
15) What do you mean by ensemble learning?
Numerous models, such as classifiers are strategically made and combined to solve a specific computational program which is known as ensemble learning. The ensemble methods are also known as committee-based learning or learning multiple classifier systems. It trains various hypotheses to fix the same issue. One of the most suitable examples of ensemble modeling is the random forest trees where several decision trees are used to predict outcomes. It is used to improve the classification, function approximation, prediction, etc. of a model.
16) What is a model selection in Machine Learning?
The process of choosing models among diverse mathematical models, which are used to define the same data is known as Model Selection. Model learning is applied to the fields of statistics, data mining, and machine learning.
17) What are the three stages of building the hypotheses or model in machine learning?
There are three stages to build hypotheses or model in machine learning:
- Model building
It chooses a suitable algorithm for the model and trains it according to the requirement of the problem. - Applying the model
It is responsible for checking the accuracy of the model through the test data. - Model testing
It performs the required changes after testing and apply the final model.
18) What according to you, is the standard approach to supervised learning?
In supervised learning, the standard approach is to split the set of example into the training set and the test.
19) Describe 'Training set' and 'training Test'.
In various areas of information of machine learning, a set of data is used to discover the potentially predictive relationship, which is known as 'Training Set'. The training set is an example that is given to the learner. Besides, the 'Test set' is used to test the accuracy of the hypotheses generated by the learner. It is the set of instances held back from the learner. Thus, the training set is distinct from the test set.
20) What are the common ways to handle missing data in a dataset?
Missing data is one of the standard factors while working with data and handling. It is considered as one of the greatest challenges faced by the data analysts. There are many ways one can impute the missing values. Some of the common methods to handle missing data in datasets can be defined as deleting the rows, replacing with mean/median/mode, predicting the missing values, assigning a unique category, using algorithms that support missing values, etc.
21) What do you understand by ILP?
ILP stands for Inductive Logic Programming. It is a part of machine learning which uses logic programming. It aims at searching patterns in data which can be used to build predictive models. In this process, the logic programs are assumed as a hypothesis.
22) What are the necessary steps involved in Machine Learning Project?
There are several essential steps we must follow to achieve a good working model while doing a Machine Learning Project. Those steps may include parameter tuning, data preparation, data collection, training the model, model evaluation, and prediction, etc.
23) Describe Precision and Recall?
Precision and Recall both are the measures which are used in the information retrieval domain to measure how good an information retrieval system reclaims the related data as requested by the user.
Precision can be said as a positive predictive value. It is the fraction of relevant instances among the received instances.
On the other side, recall is the fraction of relevant instances that have been retrieved over the total amount or relevant instances. The recall is also known as sensitivity.
24) What do you understand by Decision Tree in Machine Learning?
Decision Trees can be defined as the Supervised Machine Learning, where the data is continuously split according to a certain parameter. It builds classification or regression models as similar as a tree structure, with datasets broken up into ever smaller subsets while developing the decision tree. The tree can be defined by two entities, namely decision nodes, and leaves. The leaves are the decisions or the outcomes, and the decision nodes are where the data is split. Decision trees can manage both categorical and numerical data.
25) What are the functions of Supervised Learning?
- Classification
- Speech Recognition
- Regression
- Predict Time Series
- Annotate Strings
26) What are the functions of Unsupervised Learning?
- Finding clusters of the data
- Finding low-dimensional representations of the data
- Finding interesting directions in data
- Finding novel observations/ database cleaning
- Finding interesting coordinates and correlations
27) What do you understand by algorithm independent machine learning?
Algorithm independent machine learning can be defined as machine learning, where mathematical foundations are independent of any particular classifier or learning algorithm.
28) Describe the classifier in machine learning.
A classifier is a case of a hypothesis or discrete-valued function which is used to assign class labels to particular data points. It is a system that inputs a vector of discrete or continuous feature values and outputs a single discrete value, the class.
29) What do you mean by Genetic Programming?
Genetic Programming (GP) is almost similar to an Evolutionary Algorithm, a subset of machine learning. Genetic programming software systems implement an algorithm that uses random mutation, a fitness function, crossover, and multiple generations of evolution to resolve a user-defined task. The genetic programming model is based on testing and choosing the best option among a set of results.
30) What is SVM in machine learning? What are the classification methods that SVM can handle?
SVM stands for Support Vector Machine. SVM are supervised learning models with an associated learning algorithm which analyze the data used for classification and regression analysis.
The classification methods that SVM can handle are:
- Combining binary classifiers
- Modifying binary to incorporate multiclass learning
31) How will you explain a linked list and an array?
An array is a datatype which is widely implemented as a default type, in almost all the modern programming languages. It is used to store data of a similar type.
But there are many use-cases where we don't know the quantity of data to be stored. For such cases, advanced data structures are required, and one such data structure is linked list.
There are some points which explain how the linked list is different from an array:
| ARRAY | LINKED LIST |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32) What do you understand by the Confusion Matrix?
A confusion matrix is a table which is used for summarizing the performance of a classification algorithm. It is also known as the error matrix.
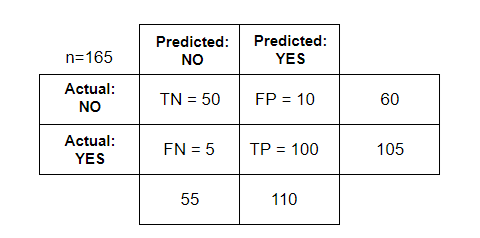
Where,
TN= True Negative
TP= True Positive
FN= False Negative
FP= False Positive
TP= True Positive
FN= False Negative
FP= False Positive
33) Explain True Positive, True Negative, False Positive, and False Negative in Confusion Matrix with an example.
- True Positive
When a model correctly predicts the positive class, it is said to be a true positive.
For example, Umpire gives a Batsman NOT OUT when he is NOT OUT. - True Negative
When a model correctly predicts the negative class, it is said to be a true negative.
For example, Umpire gives a Batsman OUT when he is OUT. - False Positive
When a model incorrectly predicts the positive class, it is said to be a false positive. It is also known as 'Type I' error.
For example, Umpire gives a Batsman NOT OUT when he is OUT. - False Negative
When a model incorrectly predicts the negative class, it is said to be a false negative. It is also known as 'Type II' error.
For example, Umpire gives a Batsman OUT when he is NOT OUT.
34) What according to you, is more important between model accuracy and model performance?
Model accuracy is a subset of model performance. The accuracy of the model is directly proportional to the performance of the model. Thus, better the performance of the model, more accurate are the predictions.
35) What is Bagging and Boosting?
- Bagging is a process in ensemble learning which is used for improving unstable estimation or classification schemes.
- Boosting methods are used sequentially to reduce the bias of the combined model.
36) What are the similarities and differences between bagging and boosting in Machine Learning?
Similarities of Bagging and Boosting
- Both are the ensemble methods to get N learns from 1 learner.
- Both generate several training data sets with random sampling.
- Both generate the final result by taking the average of N learners.
- Both reduce variance and provide higher scalability.
Differences between Bagging and Boosting
- Although they are built independently, but for Bagging, Boosting tries to add new models which perform well where previous models fail.
- Only Boosting determines the weight for the data to tip the scales in favor of the most challenging cases.
- Only Boosting tries to reduce bias. Instead, Bagging may solve the problem of over-fitting while boosting can increase it.
37) What do you understand by Cluster Sampling?
Cluster Sampling is a process of randomly selecting intact groups within a defined population, sharing similar characteristics. Cluster sample is a probability where each sampling unit is a collection or cluster of elements.
For example, if we are clustering the total number of managers in a set of companies, in that case, managers (sample) will represent elements and companies will represent clusters.
38) What do you know about Bayesian Networks?
Bayesian Networks also referred to as 'belief networks' or 'casual networks', are used to represent the graphical model for probability relationship among a set of variables.
For example, a Bayesian network can be used to represent the probabilistic relationships between diseases and symptoms. As per the symptoms, the network can also compute the probabilities of the presence of various diseases.
Efficient algorithms can perform inference or learning in Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks which relate the variables (e.g., speech signals or protein sequences) are called dynamic Bayesian networks.
39) Which are the two components of Bayesian logic program?
A Bayesian logic program consists of two components:
- Logical
It contains a set of Bayesian Clauses, which capture the qualitative structure of the domain. - Quantitative
It is used to encode quantitative information about the domain.
40) Describe dimension reduction in machine learning.
Dimension reduction is the process which is used to reduce the number of random variables under considerations.
Dimension reduction can be divided into feature selection and extraction.
41) Why instance-based learning algorithm sometimes referred to as Lazy learning algorithm?
In machine learning, lazy learning can be described as a method where induction and generalization processes are delayed until classification is performed. Because of the same property, an instance-based learning algorithm is sometimes called lazy learning algorithm.
42) What do you understand by the F1 score?
The F1 score represents the measurement of a model's performance. It is referred to as a weighted average of the precision and recall of a model. The results tending to 1 are considered as the best, and those tending to 0 are the worst. It could be used in classification tests, where true negatives don't matter much.
43) How is a decision tree pruned?
Pruning is said to occur in decision trees when the branches which may consist of weak predictive power are removed to reduce the complexity of the model and increase the predictive accuracy of a decision tree model. Pruning can occur bottom-up and top-down, with approaches such as reduced error pruning and cost complexity pruning.
Reduced error pruning is the simplest version, and it replaces each node. If it is unable to decrease predictive accuracy, one should keep it pruned. But, it usually comes pretty close to an approach that would optimize for maximum accuracy.
44) What are the Recommended Systems?
Recommended System is a sub-directory of information filtering systems. It predicts the preferences or rankings offered by a user to a product. According to the preferences, it provides similar recommendations to a user. Recommendation systems are widely used in movies, news, research articles, products, social tips, music, etc.
45) What do you understand by Underfitting?
Underfitting is an issue when we have a low error in both the training set and the testing set. Few algorithms work better for interpretations but fail for better predictions.
46) When does regularization become necessary in Machine Learning?
Regularization is necessary whenever the model begins to overfit/ underfit. It is a cost term for bringing in more features with the objective function. Hence, it tries to push the coefficients for many variables to zero and reduce cost term. It helps to reduce model complexity so that the model can become better at predicting (generalizing).
47) What is Regularization? What kind of problems does regularization solve?
A regularization is a form of regression, which constrains/ regularizes or shrinks the coefficient estimates towards zero. In other words, it discourages learning a more complex or flexible model to avoid the risk of overfitting. It reduces the variance of the model, without a substantial increase in its bias.
Regularization is used to address overfitting problems as it penalizes the loss function by adding a multiple of an L1 (LASSO) or an L2 (Ridge) norm of weights vector w.
48) Why do we need to convert categorical variables into factor? Which functions are used to perform the conversion?
Most Machine learning algorithms require number as input. That is why we convert categorical values into factors to get numerical values. We also don't have to deal with dummy variables.
The functions factor() and as.factor() are used to convert variables into factors.
49) Do you think that treating a categorical variable as a continuous variable would result in a better predictive model?
For a better predictive model, the categorical variable can be considered as a continuous variable only when the variable is ordinal in nature.
50) How is machine learning used in day-to-day life?
Most of the people are already using machine learning in their everyday life. Assume that you are engaging with the internet, you are actually expressing your preferences, likes, dislikes through your searches. All these things are picked up by cookies coming on your computer, from this, the behavior of a user is evaluated. It helps to increase the progress of a user through the internet and provide similar suggestions.
The navigation system can also be considered as one of the examples where we are using machine learning to calculate a distance between two places using optimization techniques. Surely, people are going to more engage with machine learning in the near future.


