SQL Interview Questions
1) What is SQL?
SQL stands for the Structured Query Language. SQL is a standard query language used for maintaining the relational database and perform many different operations of data manipulation on the data. SQL initially was invented in 1970. It is a database language used for database creation, deletion, fetching rows and modifying rows, etc. sometimes it is pronounced as 'sequel.'
2) When SQL appeared?
It appeared in 1974. SQL is one of the often used languages for maintaining the relational database. SQL. In 1986 SQL become the standard of American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and ISO(International Organization for Standardization) in 1987.
3) What are the usages of SQL?
- SQL is responsible for maintaining the relational data and the data structures present in the database.
- To execute queries against a database
- To retrieve data from a database
- To inserts records in a database
- To updates records in a database
- To delete records from a database
- To create new databases
- To create new tables in a database
- To create views in a database
- To perform complex operations on the database.
4) Does SQL support programming?
SQL refers to the Standard Query Language, which is not actually the programming language. SQL doesn't have a loop, Conditional statement, logical operations, it can not be used for anything other than data manipulation. It is used like commanding (Query) language to access databases. The primary purpose of SQL is to retrieve, manipulate, update and perform complex operations like joins on the data present in the database.
5) What are the subsets of SQL?
There is three significant subset of the SQL:
- Data definition language (DDL):DDL is used to define the data structure it consists of the commands like CREATE, ALTER, DROP, etc.
- Data manipulation language (DML):DML is used to manipulate already existing data in the database. The commands in this category are SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, etc.
- Data control language (DCL):DCL is used to control access to data in the database and includes commands such as GRANT, REVOKE.
6) What is a Data Definition Language?
Data definition language (DDL) is the subset of the database which defines the data structure of the database in the initial stage when the database is about to be created. It consists of the following commands: CREATE, ALTER and DELETE database objects such as schema, tables, view, sequence, etc.
7) What is a Data Manipulation Language?
Data manipulation language makes the user able to retrieve and manipulate data. It is used to perform the following operations.
- Insert data into database through INSERT command.
- Retrieve data from the database through SELECT command.
- Update data in the database through UPDATE command.
- Delete data from the database through DELETE command.
8) What is Data Control Language?
Data control language allows you to control access to the database. DCL is the only subset of the database which decides that what part of the database should be accessed by which user at what point of time. It includes two commands GRANT and REVOKE.
GRANT: to grant the specific user to perform a particular task
REVOKE: to cancel previously denied or granted permissions.
9) What are tables and fields in the database?
A table is a set of organized data. It has rows and columns. Rows here refers to the tuples which represent the simple data item and columns are the attribute of the data items present in particular row. Columns can categorize as vertical, and Rows are horizontal.
A table contains a specified number of the column called fields but can have any number of rows which is known as the record. So, the columns in the table of the database are known as the fields and they represent the attribute or characteristics of the entity in the record.
10) What is a primary key?
A primary key is a field or the combination of fields which uniquely specify a row. The Primary key is a special kind of unique key. Primary key values cannot be NULL. For example, the Social Security Number can be treated as the primary key for any individual.
11) What is a foreign key?
A foreign key is specified as a key which is related to the primary key of another table. A relationship needs to be created between two tables by referencing foreign key with the primary key of another table. Foreign key acts like a cross-reference between tables as it refers to the primary key of other table and the primary key-foreign key relationship is a very crucial relationship as it maintains the ACID properties of database sometimes.
12) What is a unique key?
Unique key constraint uniquely identifies each record in the database. This key provides uniqueness for the column or set of columns.
The Unique key cannot accept a duplicate value.
The unique key can accept only on Null value.
13) What is the difference between primary key and unique key?
Primary key and unique key both are the essential constraints of the SQL, but there is a small difference between them
Primary key carries unique value but the field of the primary key cannot be Null on the other hand unique key also carry unique value but it can have a single Null value field.
14) What is a Database?
A Database is an organized form of data. The database is the electronic system which makes data access, data manipulation, data retrieval, data storing and data management very easy and structured. Almost every organization uses the database for storing the data due to its easily accessible and high operational ease. The database provides perfect access to data and lets us perform required tasks.
The Database is also called a structured form of data. Due to this structured format, you can access data very easily.
15) What is DBMS?
DBMS stands for Database Management System. This is a program which is used to control them. It is like a File Manager that manages data in a database rather than saving it in file systems.
Database management system is an interface between the database and the user. It makes the data retrieval, data access easier.
Database management system is a software which provides us the power to perform operations such as creation, maintenance and use of a data of the database using a simple query in almost no time.
Without the database management system, it would be far more difficult for the user to access the data of the database.
16) What are the different types of database management systems?
There are four types of database:
- Hierarchical databases (DBMS)
- Relational databases (RDBMS)
- Network databases (IDMS)
- Object-oriented databases
RDBMS is one of the most often used databases due to its easy accessibility and supports regarding complex queries.
17) What is RDBMS?
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. It is a database management system based on a relational model. RDBMS stores the data into the collection of tables and links those table using the relational operators easily whenever required. It facilitates you to manipulate the data stored in the tables by using relational operators. Examples of the relational database management system are Microsoft Access, MySQL, SQLServer, Oracle database, etc.
18) What is Normalization in a Database?
Normalization is used to minimize redundancy and dependency by organizing fields and table of a database.
There are some rules of database normalization which commonly known as Normal From and they are:
- First normal form(1NF)
- Second normal form(2NF)
- Third normal form(3NF)
- Boyce-Codd normal form(BCNF)
Using these steps, the redundancy, anomalies, inconsistency of the data in the database can be removed.
19) What is the primary use of Normalization?
Normalization is mainly used to add, delete or modify a field that can be made in a single table. The primary use of Normalization is to remove redundancy and to remove the insert, delete and update distractions. Normalization breaks the table into small partitions and then link them using different relationships so that it will avoid the chances of redundancy.
20) What are the disadvantages of not performing Database Normalization?
The major disadvantages are:
- The occurrence of redundant terms in the database which causes the waste of the space in the disk.
- Due to redundant terms inconsistency may also occur id any change will be made in the data of one table but not made in the same data of another table then inconsistency will take place, which will lead to the maintenance problem and effects the ACID properties as well.
21) What is an inconsistent dependency?
Inconsistent dependency refers to the difficulty of accessing particular data as the path to reach the data may be missing or broken. Inconsistent dependency will leads users to search the data in the wrong table which will afterward give the error as an output.
22) What is Denormalization in a Database?
Denormalization is used to access the data from higher or lower normal form of database. It also processes redundancy into a table by incorporating data from the related tables. Denormalization adds required redundant term into the tables so that we can avoid using complex joins and many other complex operations. Denormalization doesn?t mean that normalization will not be done, but the denormalization process takes place after the normalization process.
23) What are the types of operators available in SQL?
Operators are the special keywords or special characters reserved for performing particular operations and are used in the SQL queries. There is three type of operators used in SQL:
- Arithmetic operators: addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), etc.
- Logical operators: ALL, AND, ANY, ISNULL, EXISTS, BETWEEN, IN, LIKE, NOT, OR, UNIQUE.
- Comparison operator: =, !=, <>, <, >, <=, >=, !<, !>
24) What is view in SQL?
A view is a virtual table which contains a subset of data within a table. Views are not originally present, and it takes less space to store. A view can have data from one or more tables combined, and it depends on the relationship. Views are used to apply security mechanism in the SQL Server. The view of the database is the searchable object we can use a query to search the view as we use for the table.
25) What is an Index in SQL?
SQL indexes are the medium of reducing the cost of the query as the high cost of the query will lead to the fall in the performance of the query. An index is used to increase the performance and allow faster retrieval of records from the table. Indexing reduces the number of data pages we need to visit to find a particular data page. Indexing also has a unique value that means that the index cannot be duplicated. An index creates an entry for each value, and it will be faster to retrieve data. For example, suppose you have a book which carries the details of the countries, and you want to find out the information about India than why you will go through every page of that book you could directly go to the index, and then from index you can go to that particular page where all the information about India is given.
26) Which are the different types of indexes in SQL?
There are three types of Indexes in SQL:
- Unique Index
- Clustered Index
- NonClustered Index
- Bit-Map index
- Normal index
- Composite index
- B-tree index
- function based index
27) What is the unique Index?
Unique Index:
For creating a unique index, the user has to check the data in the column because the unique indexes are used when any column of the table has unique values. This indexing does not allow the field to have duplicate values if the column is unique indexed. A unique index can be applied automatically when a primary key is defined.
28) What is Clustered Index in SQL?
Clustered Index:
The clustered index is used to reorder the physical order of the table and search based on the key values. Each table can have only one clustered index. The Clustered index is the only index which has been automatically created when the primary key is generated. If moderate data modification needed to be done in the table then clustered indexes are preferred.
29) What is the Non-Clustered Index in SQL?
Non-Clustered Index:
The reason to create non-clustered index is searching the data. We well know that clustered indexes are created automatically primary keys are generated, but non-clustered indexes are created when multiple joins conditions and various filters are used in the query. Non-Clustered Index does not alter the physical order of the table and maintains logical order of data. Each table can have 999 non-clustered indexes.
30) What is the difference between SQL, MySQL and SQL Server?
SQL or Structured Query Language is a language which is used to communicate with a relational database. It provides a way to manipulate and create databases. On the other hand, MySQL and Microsoft's SQL Server both are relational database management systems that use SQL as their standard relational database language.
MySQL is available for free as it is open source whereas SQL server is not an open source software.
31) What is the difference between SQL and PL/SQL?
SQL or Structured Query Language is a language which is used to communicate with a relational database. It provides a way to manipulate and create databases. On the other hand, PL/SQL is a dialect of SQL which is used to enhance the capabilities of SQL. It was developed by Oracle Corporation in the early 90's. It adds procedural features of programming languages in SQL.
In SQL single query is being executed at once whereas in PL/SQL a whole block of code is executed at once.
SQL is like the source of data that we need to display on the other hand PL/SQL provides a platform where the SQL the SQL data will be shown.
SQL statement can be embedded in PL/SQL, but PL/SQL statement cannot be embedded in SQL as SQL do not support any programming language and keywords.
32) Is it possible to sort a column using a column alias?
Yes. You can use the column alias in the ORDER BY instead of WHERE clause for sorting.
33) What is the difference between clustered and non-clustered index in SQL?
There are mainly two type of indexes in SQL, Clustered index and non clustered index. The differences between these two indexes is very important from SQL performance perspective.
- One table can have only one clustered index, but it can have many non-clustered index. (Approximately 250).
- A clustered index determines how data is stored physically in the table. Clustered index stores data in the cluster, related data is stored together, so that retrieval of data becomes simple.
- Clustered indexes store the data information and the data itself whereas non-clustered index stores only the information, and then it will refer you to the data stored in clustered data.
- Reading from a clustered index is much faster than reading from non-clustered index from the same table.
- Clustered index sort and store data row in the table or view based on their key value, while non-cluster has a structure separate from the data row.
34) What is the SQL query to display the current date?
There is a built-in function in SQL called GetDate() which is used to return the current timestamp.
35) Which are the most commonly used SQL joins?
Most commonly used SQL joins are INNER JOIN and LEFT OUTER JOIN and RIGHT OUTER JOIN.
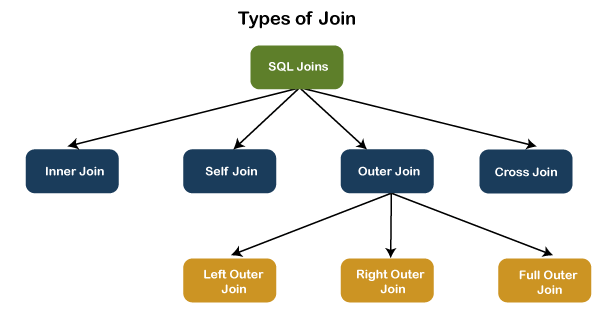
36) What are the different types of joins in SQL?
Joins are used to merge two tables or retrieve data from tables. It depends on the relationship between tables.
Following are the most commonly used joins in SQL:
Inner Join: inner joins are of three type:
- Theta join
- Natural join
- Equijoin
Outer Join: outer joins are of three type:
- right outer join
- Left outer join
- Full outer join
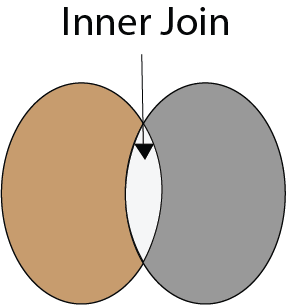
37) What is Inner Join in SQL?
Inner join:
Inner join returns rows when there is at least one match of rows between the tables. INNER JOIN keyword joins the matching records from two tables.
INNER JOIN
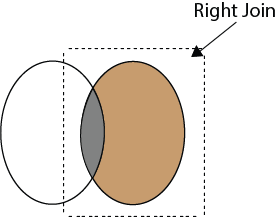
38) What is Right Join in SQL?
Right Join:
Right Join is used to retrieve rows which are common between the tables and all rows of a Right-hand side table. It returns all the rows from the right-hand side table even though there are no matches in the left-hand side table.
RIGHT JOIN
39) What is Left Join in SQL?
Left Join:
The left join is used to retrieve rows which are common between the tables and all rows of the Left-hand side table. It returns all the rows from the Left-hand side table even though there are no matches on the Right-hand side table.
LEFT JOIN
40) What is Full Join in SQL?
Full Join:
Full join return rows when there are matching rows in any one of the tables. This means it returns all the rows from the left-hand side table and all the rows from the right-hand side table.
FULL OUTER JOIN
41) What is a "TRIGGER" in SQL?
- A trigger allows you to execute a batch of SQL code when an insert, update or delete command is run against a specific table as TRIGGER is said to be the set of actions that are performed whenever commands like insert, update or delete are given through queries.
- The trigger is said to be activated when these commands are given to the system.
- Triggers are the particular type of stored procedures that are defined to execute automatically in place or after data modifications.
- Triggers are generated using CREATE TRIGGER statement.
42) What is self-join and what is the requirement of self-join?
A self-join is often very useful to convert a hierarchical structure to a flat structure. It is used to join a table to itself as like if that is the second table.
43) What are the set operators in SQL?
SQL queries which contain set operations are called compound queries.
Union, Union All, Intersect or Minus operators are the set operators used in the SQL.
44) What is the difference between BETWEEN and IN condition operators?
The BETWEEN operator is used to display rows based on a range of values. The values can be numbers, text, and dates as well. BETWEEN operator gives us the count of all the values occurs between a particular range.
The IN condition operator is used to check for values contained in a specific set of values. IN operator is used when we have more than one value to choose.
45) What is a constraint? Tell me about its various levels.
Constraints are the rules and regulations which are applied to the table column which enforces yours to store valid data and prevents users to store irrelevant data. There are two levels :
- column level constraint
- table level constraint
46) Write an SQL query to find names of employee start with 'A'?
- SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE EmpName like 'A%'
47) Write an SQL query to get the third maximum salary of an employee from a table named employee_table.
- SELECT TOP 1 salary
- FROM (
- SELECT TOP 3 salary
- FROM employee_table
- ORDER BY salary DESC ) AS emp
- ORDER BY salary ASC;
48) What is the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE statement in SQL?
The main differences between SQL DELETE and TRUNCATE statements are given below:
| No. | DELETE | TRUNCATE |
|---|---|---|
| 1) | DELETE is a DML command. | TRUNCATE is a DDL command. |
| 2) | We can use WHERE clause in DELETE command. | We cannot use WHERE clause with TRUNCATE |
| 3) | DELETE statement is used to delete a row from a table | TRUNCATE statement is used to remove all the rows from a table. |
| 4) | DELETE is slower than TRUNCATE statement. | TRUNCATE statement is faster than DELETE statement. |
| 5) | You can rollback data after using DELETE statement. | It is not possible to rollback after using TRUNCATE statement. |
49) What is ACID property in a database?
ACID property is used to ensure that the data transactions are processed reliably in a database system.
A single logical operation of a data is called transaction.
ACID is an acronym for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability.
Atomicity: it requires that each transaction is all or nothing. It means if one part of the transaction fails, the entire transaction fails and the database state is left unchanged.
Consistency: the consistency property ensure that the data must meet all validation rules. In simple words you can say that your transaction never leaves your database without completing its state.
Isolation: this property ensure that the concurrent property of execution should not be met. The main goal of providing isolation is concurrency control.
Durability: durability simply means that once a transaction has been committed, it will remain so, come what may even power loss, crashes or errors.
50) What is the difference between NULL value, zero and blank space?
Ans: A NULL value is not the same as zero or a blank space. A NULL value is a value which is 'unavailable, unassigned, unknown or not applicable.' On the other hand, zero is a number, and a blank space is treated as a character.
The NULL value can be treated as unknown and missing value as well, but zero and blank spaces are different from the NULL value.
51) What is the usage of SQL functions?
Functions are the measured values and cannot create permanent environment changes to SQL server. SQL functions are used for the following purpose:
- To perform calculations on data
- To modify individual data items
- To manipulate the output
- To format dates and numbers
- To convert data types
52) What do you understand by case manipulation functions?
Case manipulation functions are the functions which convert the data from the state in which it is already stored in the table to upper, lower or mixed case.
Case manipulation function can be used in almost every part of the SQL statement.
Case manipulation functions are mostly used when you need to search for data, and you don?t have any idea that the data you are looking for is in lower case or upper case.
53) Which are the different case manipulation functions in SQL?
There are three case manipulation functions in SQL:
- LOWER: converts character into Lowercase.
- UPPER: converts character into uppercase.
- INITCAP: converts character values to uppercase for the initials of each word.
54) Explain character-manipulation functions?
Character-manipulation functions are used to change, extract, alter the character string.
One or more than one characters and words should be passed into the function, and then the function will perform its operation on those words.
55) Which are the different character-manipulation functions in SQL?
- CONCAT: join two or more values together.
- SUBSTR: used to extract the string of specific length.
- LENGTH: return the length of the string in numerical value.
- INSTR: find the exact numeric position of a specified character.
- LPAD: padding of the left-side character value for right-justified value.
- RPAD: padding of right-side character value for left-justified value.
- TRIM: remove all the defined character from the beginning, end or both beginning and end.
- REPLACE: replace a specific sequence of character with other sequences of character.
56) What is the usage of NVL() function?
The NVL() function is used to convert NULL value to the other value. NVL() function is used in Oracle it is not in SQL and MySQL server.
Instead of NVL() function MySQL have IFNULL() and SQL Server have ISNULL() function.
57) Which function is used to return remainder in a division operator in SQL?
The MOD function returns the remainder in a division operation.
58) What are the syntax and use of the COALESCE function?
The syntax of COALESCE function:
- COALESCE(exp1, exp2, .... expn)
The COALESCE function is used to return the first non-null expression given in the parameter list.
59) What is the usage of the DISTINCT keyword?
The DISTINCT keyword is used to ensure that the fetched value is only a non-duplicate value. The DISTINCT keyword is used to SELECT DISTINCT, and it always fetches different (distinct) from the column of the table.
Query of SQL
COMMANDS
ALTER TABLE
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD column_name datatype;
ALTER TABLE lets you add columns to a table in a database.AND
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_1 = value_1
AND column_2 = value_2;
AND is an operator that combines two conditions. Both conditions must be true for the row to be included in the result set.AS
SELECT column_name AS 'Alias'
FROM table_name;
AS is a keyword in SQL that allows you to rename a column or table using an alias.AVG()
SELECT AVG(column_name)
FROM table_name;
AVG() is an aggregate function that returns the average value for a numeric column.BETWEEN
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name BETWEEN value_1 AND value_2;
The
BETWEEN operator is used to filter the result set within a certain range. The values can be numbers, text or dates.CASE
SELECT column_name,
CASE
WHEN condition THEN 'Result_1'
WHEN condition THEN 'Result_2'
ELSE 'Result_3'
END
FROM table_name;
CASE statements are used to create different outputs (usually in the SELECT statement). It is SQL’s way of handling if-then logic.COUNT()
SELECT COUNT(column_name)
FROM table_name;
COUNT() is a function that takes the name of a column as an argument and counts the number of rows where the column is not NULL.CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column_1 datatype,
column_2 datatype,
column_3 datatype
);
CREATE TABLE creates a new table in the database. It allows you to specify the name of the table and the name of each column in the table.DELETE
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE some_column = some_value;
DELETE statements are used to remove rows from a table.GROUP BY
SELECT column_name, COUNT(*)
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column_name;
GROUP BY is a clause in SQL that is only used with aggregate functions. It is used in collaboration with the SELECT statement to arrange identical data into groups.HAVING
SELECT column_name, COUNT(*)
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column_name
HAVING COUNT(*) > value;
HAVING was added to SQL because the WHERE keyword could not be used with aggregate functions.INNER JOIN
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_1
JOIN table_2
ON table_1.column_name = table_2.column_name;
An inner join will combine rows from different tables if the join condition is true.
INSERT
INSERT INTO table_name (column_1, column_2, column_3)
VALUES (value_1, 'value_2', value_3);
INSERT statements are used to add a new row to a table.IS NULL / IS NOT NULL
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name IS NULL;
IS NULL and IS NOT NULL are operators used with the WHERE clause to test for empty values.LIKE
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name LIKE pattern;
LIKE is a special operator used with the WHERE clause to search for a specific pattern in a column.LIMIT
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
LIMIT number;
LIMIT is a clause that lets you specify the maximum number of rows the result set will have.MAX()
SELECT MAX(column_name)
FROM table_name;
MAX() is a function that takes the name of a column as an argument and returns the largest value in that column.MIN()
SELECT MIN(column_name)
FROM table_name;
MIN() is a function that takes the name of a column as an argument and returns the smallest value in that column.OR
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name = value_1
OR column_name = value_2;
OR is an operator that filters the result set to only include rows where either condition is true.ORDER BY
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name
ORDER BY column_name ASC | DESC;
ORDER BY is a clause that indicates you want to sort the result set by a particular column either alphabetically or numerically.OUTER JOIN
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_1
LEFT JOIN table_2
ON table_1.column_name = table_2.column_name;
An outer join will combine rows from different tables even if the join condition is not met. Every row in the left table is returned in the result set, and if the join condition is not met, then
NULL values are used to fill in the columns from the right table.ROUND()
SELECT ROUND(column_name, integer)
FROM table_name;
ROUND() is a function that takes a column name and an integer as arguments. It rounds the values in the column to the number of decimal places specified by the integer.SELECT
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name;
SELECT statements are used to fetch data from a database. Every query will begin with SELECT.SELECT DISTINCT
SELECT DISTINCT column_name
FROM table_name;
SELECT DISTINCT specifies that the statement is going to be a query that returns unique values in the specified column(s).SUM
SELECT SUM(column_name)
FROM table_name;
SUM() is a function that takes the name of a column as an argument and returns the sum of all the values in that column.UPDATE
UPDATE table_name
SET some_column = some_value
WHERE some_column = some_value;
UPDATE statements allow you to edit rows in a table.WHERE
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name operator value;
WHERE is a clause that indicates you want to filter the result set to include only rows where the following condition is true.WITH
WITH temporary_name AS (
SELECT *
FROM table_name)
SELECT *
FROM temporary_name
WHERE column_name operator value;
WITH clause lets you store the result of a query in a temporary table using an alias. You can also define multiple temporary tables using a comma and with one instance of the WITH keyword.

